How to fill water into an open and closed heating system? How to fill the heating system with coolant How to fill the heating system correctly.
What liquids can be used as a coolant? How to start the heating for the first time after its installation is completed? What should be the operating pressure of a cottage heating system? Today we have to answer these and some other questions.
Selection of coolant
First, a few words about what liquids can be used to fill the heating system. Here are the key properties of popular coolants.
Water
- Price: minimal (when pumped from a water supply with a water meter installed at the entrance to the house - from 20 rubles per cubic meter);
- Heat capacity: high (4183 J/(kg deg) at +20°C);
- Viscosity: low (meaning low load on the circulation pump);
- Corrosivity: medium (steel in contact with water rusts only in the presence of oxygen);
- Toxicity: absent;
- : 0.03%/deg.

Antifreeze
Antifreeze was developed several decades ago as a winter filler for water cooling systems of automobile engines. Nowadays, it is often used as a winter coolant. The numerical designation in the marking of antifreeze (30, 40 or 65) means its freezing temperature.
- Price: from 40 rubles per kilogram for wholesale supplies and from 60 for retail sales;
- Heat capacity: average (3520 J/(kg deg));
- Viscosity: high (the load on the pump increases due to an increase in the hydraulic resistance of the system);
- Corrosivity: low due to anti-corrosion additives;
- Toxicity: high (the original antifreeze contains poisonous ethylene glycol);
- Heat expansion coefficient: 0.05%/deg. The higher the expansion coefficient, the larger the expansion tank must be in a closed heating system. It is this that compensates for the expansion of the coolant as the temperature rises.

Due to zero corrosive activity, antifreeze creates leaks at the slightest violation of the tightness of the heating circuit. Water and other coolants quickly clog small leaks with rust and crystallizing mineral salts.
Propylene glycol
Non-freezing coolants are produced on the basis of propylene glycol, designed specifically for heating systems.

- Price: from 100 rubles per kilogram;
- Heat capacity: low (2400 J/(kg deg));
Propylene glycol is used in the form of an aqueous solution. Mixing with water increases its heat capacity to the level of antifreeze (3500-4000 J/(kg deg) depending on the proportion of the mixture).
- Viscosity: high;
- Corrosivity: low due to additives;
- Toxicity: zero (canisters with coolant are marked green and marked “Eco”);

- Heat expansion coefficient: approximately 0.05%/deg.
Brine
A concentrated solution of table salt, calcium chloride and other salts can also be used as a coolant: its freezing point is inversely proportional to the salt concentration. These are a typical budget solution, which is limited to use only in open systems with natural circulation.
- Price: from 5 rubles per 1 kg of table salt;
- Heat capacity: low (at 30 percent concentration - 2700 J/(kg deg);
- Viscosity: low;
- Corrosivity: extremely high. Salt literally corrodes steel pipes;

- Toxicity: null;
- Expansion when heated: approximately 0.03%/deg.
At high brine concentrations and slow movement of the coolant in the system, excess salts will gradually be deposited on the walls of the pipes, reducing their cross-section. In a forced circulation circuit, brine has a detrimental effect on the pump: the shaft and impeller become overgrown with crystals, which leads to a drop in performance.
conclusions
The instructions for choosing a coolant are quite obvious:
- If you have the opportunity to maintain a positive temperature in your house throughout the heating season, it is best to fill the heating circuit with water. It is better to use distilled water, but you can also use drinking water or even well water;
- If the cottage is periodically left without heating, your choice is non-freezing coolants based on propylene glycol.

A time to reset and a time to fill
When do you have to fill the heating circuit?
In just three cases:
- On first launch;
- After renovation shut-off and control valves, boiler, bottling, replacement of heating devices, etc.;
- After reset heating system during long winter downtime. It is practiced if the circuit is filled with water and the house remains without heating for a long time.
To completely drain the circuit, vents must be placed on all brackets below the bottling level. When resetting, you need to open at least one vent at the top point of the circuit so that it sucks in air.

Open system
Autonomous heating can operate according to two fundamentally different schemes:
| Image | Description |
 |
Open system: operates with a pressure equal to the height of the water column between the lower and upper points of the circuit. It communicates with the atmosphere through an open expansion tank. |
 |
Closed system: operates with an excess pressure of 1.5-2.5 atmospheres. It is equipped with a membrane expansion tank that compensates for the increase in coolant volume when it is heated. |
A peculiarity of the installation of an open heating system is that its bottlings (supply and return) are laid with a constant slope from the open expansion tank at the top point of the circuit.
This pipe layout has two practical consequences:
- Pour water into the system can be done directly through the expansion tank(in buckets or through a water supply tap located in the attic);

- All the air will be forced out there, remaining in the circuit at the time of its filling.
How to run such a system with your own hands? It’s as easy as shelling pears: fill the circuit and light the boiler. If the circuit is designed to operate with natural circulation, circulation will begin immediately after the boiler heat exchanger warms up. In a system with a pump, you must additionally turn on its power.
Closed system
How to fill a closed heating system with water or antifreeze?
The fittings can provide partially automated and manual filling of a closed-type heating system. In the first case, its set looks like this:
| Image | Knot |
 |
Jumper between heating and cold water system with tap. To fill the circuit, it is enough to close all the discharge valves and open the tap. |
 |
Pressure gauge for visual monitoring of pressure in the system (it is part of the boiler safety group). |
 |
Automatic air vent. He is also part of the boiler safety team. Its function is to vent the circuit (discharge air and steam into the atmosphere). |
 |
Mayevsky cranes, installed on all heating devices and dispensing brackets above its main level . Through them, the remaining air remaining in the pockets is released. |
The safety group and expansion tank are often located in the body of a single-circuit or double-circuit boiler with electronic control. In this case, the readings of the pressure sensor, which replaces the pressure gauge, are displayed on the front display panel of the device.
When filling the circuit with water from the cold water system, most of the air is displaced through the automatic air vent of the safety group (immediately upon filling and when the circulation pump is turned on). After startup, all that remains is to bleed the air from individual devices through Mayevsky’s taps. The filling pressure is controlled by a pressure gauge.

How to properly fill a closed heating system if there is no power supply from cold water supply?
To pump water, you will need a vent installed at the top of the circuit (a ball valve pointing upward) and... a bicycle pump.
It is necessary to bleed all the air from the expansion tank through the spool, fill the circuit with water through the funnel inserted into the vent, close the vent and re-pump the expansion tank to operating pressure (1.5 kgf/cm2).

Conclusion
As you can see, starting an autonomous heating circuit is not particularly difficult. The video in this article will help you learn more about it. Feel free to add and comment on it. Good luck, comrades!
The heating system, being a complex engineering structure, consists of many elements that have different functional purposes. The expansion tank for heating is one of the most important parts of the heating system circuit.
 When the coolant is heated, the pressure in the boiler and the heating system circuit increases significantly due to the temperature increase in the volume of the coolant fluid. Considering that the liquid is a practically incompressible medium and the heating system is sealed, this physical phenomenon can lead to the destruction of the boiler or pipelines. The problem could be solved by installing a simple valve that could release the excess volume of hot coolant into the external environment, if not for one important factor.
When the coolant is heated, the pressure in the boiler and the heating system circuit increases significantly due to the temperature increase in the volume of the coolant fluid. Considering that the liquid is a practically incompressible medium and the heating system is sealed, this physical phenomenon can lead to the destruction of the boiler or pipelines. The problem could be solved by installing a simple valve that could release the excess volume of hot coolant into the external environment, if not for one important factor.
 When cooling, the liquid contracts and air enters the heating circuit in place of the discharged coolant. Air jams are a headache for any heating system; they make circulation in the network impossible. Therefore it is necessary. Constantly adding new coolant to the system is very expensive; heating cold water is much more expensive than heating the coolant that came into the boiler through the return pipeline.
When cooling, the liquid contracts and air enters the heating circuit in place of the discharged coolant. Air jams are a headache for any heating system; they make circulation in the network impossible. Therefore it is necessary. Constantly adding new coolant to the system is very expensive; heating cold water is much more expensive than heating the coolant that came into the boiler through the return pipeline.
 This problem is solved by installing a so-called expansion tank, which is a reservoir connected to the system by one pipe. Excess pressure in the heating expansion tank is compensated by its volume and allows for stable operation of the circuit. Externally, expansion tanks for the heating system, based on the calculation results and the type of heating circuit, are different in shape and size. Currently, tanks are produced in various shapes, from classic cylindrical tanks to so-called “tablets”.
This problem is solved by installing a so-called expansion tank, which is a reservoir connected to the system by one pipe. Excess pressure in the heating expansion tank is compensated by its volume and allows for stable operation of the circuit. Externally, expansion tanks for the heating system, based on the calculation results and the type of heating circuit, are different in shape and size. Currently, tanks are produced in various shapes, from classic cylindrical tanks to so-called “tablets”.
Types of heating systems
 There are two schemes for building heating networks -. An open (gravity) heating system is used in centralized heating networks and allows water to be directly withdrawn for hot water supply needs, which is impossible in private housing construction. Such a device is located at the top point of the heating system circuit. In addition to leveling pressure drops, the heating expansion tank performs the function of natural separation of air from the system, since it has the ability to communicate with the outside atmosphere.
There are two schemes for building heating networks -. An open (gravity) heating system is used in centralized heating networks and allows water to be directly withdrawn for hot water supply needs, which is impossible in private housing construction. Such a device is located at the top point of the heating system circuit. In addition to leveling pressure drops, the heating expansion tank performs the function of natural separation of air from the system, since it has the ability to communicate with the outside atmosphere.
 Thus, structurally, such a device is a compensation tank of the heating system, not under pressure. Sometimes a system with gravitational (natural) circulation of a heat-carrying fluid may be mistakenly called open, which is fundamentally incorrect.
Thus, structurally, such a device is a compensation tank of the heating system, not under pressure. Sometimes a system with gravitational (natural) circulation of a heat-carrying fluid may be mistakenly called open, which is fundamentally incorrect.
With a more modern closed circuit, an expansion tank of a closed-type heating system with a built-in internal membrane is used.
 Sometimes such a device can be called a vacuum expansion tank for heating, which is also true. Such a system provides for forced circulation of the coolant; air is removed from the circuit through special taps (valves) installed on the heating devices and at the top of the system pipelines.
Sometimes such a device can be called a vacuum expansion tank for heating, which is also true. Such a system provides for forced circulation of the coolant; air is removed from the circuit through special taps (valves) installed on the heating devices and at the top of the system pipelines.
Device and principle of operation
 A structurally closed expansion tank in a heating system is a cylindrical tank with a rubber membrane installed inside, which divides the internal volume of the vessel into air and liquid chambers.
A structurally closed expansion tank in a heating system is a cylindrical tank with a rubber membrane installed inside, which divides the internal volume of the vessel into air and liquid chambers.
Membranes are of the following types:

 Gas pressure is adjusted individually for each system, which is described in the instructions supplied with devices such as an expansion tank for closed-type heating. Some manufacturers provide the possibility of replacing the membrane in the design of their expansion tanks. This approach slightly increases the initial cost of the device, but subsequently, if the membrane is destroyed or damaged, the cost of replacing it will be lower than the price of a new expansion tank.
Gas pressure is adjusted individually for each system, which is described in the instructions supplied with devices such as an expansion tank for closed-type heating. Some manufacturers provide the possibility of replacing the membrane in the design of their expansion tanks. This approach slightly increases the initial cost of the device, but subsequently, if the membrane is destroyed or damaged, the cost of replacing it will be lower than the price of a new expansion tank.
From a practical point of view, the shape of the membrane does not in any way affect the operating efficiency of the devices; it should only be noted that a closed-type balloon expansion tank for heating holds a slightly larger volume of heat-carrying liquid.
 The principle of their operation is also the same - when the water pressure in the network increases due to expansion when heated, the membrane stretches, compressing the gas on the other side and allows excess coolant to enter the tank. When it cools down and, accordingly, the pressure in the network drops, the process occurs in the reverse order. Thus, regulation of constant pressure in the network occurs automatically.
The principle of their operation is also the same - when the water pressure in the network increases due to expansion when heated, the membrane stretches, compressing the gas on the other side and allows excess coolant to enter the tank. When it cools down and, accordingly, the pressure in the network drops, the process occurs in the reverse order. Thus, regulation of constant pressure in the network occurs automatically.
 It is necessary to focus on the fact that if you buy an expansion tank for the heating system at random, without the necessary calculations, then it will be very difficult to achieve stable operation of the heating network. If the tank size is significantly larger than necessary, the pressure required for the system will not be created. If the tank is smaller than the required size, it will not be able to accommodate the excess volume of heat-carrying liquid, which may result in an emergency situation.
It is necessary to focus on the fact that if you buy an expansion tank for the heating system at random, without the necessary calculations, then it will be very difficult to achieve stable operation of the heating network. If the tank size is significantly larger than necessary, the pressure required for the system will not be created. If the tank is smaller than the required size, it will not be able to accommodate the excess volume of heat-carrying liquid, which may result in an emergency situation.
Calculation of expansion tanks
 To calculate an expansion tank for closed-type heating, you first need to calculate the total volume of the system, consisting of the volumes of the circuit pipelines, heating boiler and heating appliances. The volumes of the boiler and heating radiators are indicated in their passports, and the volume of pipelines is determined by multiplying the internal cross-sectional area of the pipes by their length. If the system contains pipelines of different diameters, then their volumes should be determined separately and then added together.
To calculate an expansion tank for closed-type heating, you first need to calculate the total volume of the system, consisting of the volumes of the circuit pipelines, heating boiler and heating appliances. The volumes of the boiler and heating radiators are indicated in their passports, and the volume of pipelines is determined by multiplying the internal cross-sectional area of the pipes by their length. If the system contains pipelines of different diameters, then their volumes should be determined separately and then added together.
Further calculations for devices such as an expansion tank for closed-type heating are carried out using the formula V = (Vc x k) / D, where:
 Vс – volume of heat-carrying fluid in the heating system,
Vс – volume of heat-carrying fluid in the heating system,
k – coefficient volumetric thermal expansion, taken for water 4%, for 10% ethylene glycol - 4.4%, for 20% ethylene glycol - 4.8%;
D is an indicator of the efficiency of the membrane unit. It is usually indicated by the manufacturer or can be determined by the formula: D = (Рм – Рн) / (Рм +1), where:  Рм – the maximum possible pressure in the heating network, usually it is equal to the maximum operating pressure of the safety valve (for private houses it rarely exceeds 2.5 - 3 atm.)
Рм – the maximum possible pressure in the heating network, usually it is equal to the maximum operating pressure of the safety valve (for private houses it rarely exceeds 2.5 - 3 atm.)
Рн – initial pumping pressure of the air chamber of the expansion tank, taken as 0.5 atm. for every 5 meters of height of the heating system circuit.
 In any case, it should be assumed that expansion tanks for heating should provide an increase in the volume of coolant in the network within 10%, that is, if the volume of coolant in the system is 500 liters, the volume together with the tank should be 550 liters. Accordingly, an expansion tank of the heating system with a volume of at least 50 liters is required. This method of determining volume is very approximate and can result in unnecessary costs for purchasing a larger expansion tank.
In any case, it should be assumed that expansion tanks for heating should provide an increase in the volume of coolant in the network within 10%, that is, if the volume of coolant in the system is 500 liters, the volume together with the tank should be 550 liters. Accordingly, an expansion tank of the heating system with a volume of at least 50 liters is required. This method of determining volume is very approximate and can result in unnecessary costs for purchasing a larger expansion tank.
 Currently, online calculators for calculating expansion tanks have appeared on the Internet. If such services are used to select equipment, it is necessary to carry out calculations on at least three sites to determine how correct the calculation algorithm of a particular Internet calculator is.
Currently, online calculators for calculating expansion tanks have appeared on the Internet. If such services are used to select equipment, it is necessary to carry out calculations on at least three sites to determine how correct the calculation algorithm of a particular Internet calculator is.
Manufacturers and prices
 Currently, the problem of buying an expansion tank for heating lies only in the correct selection of the type and volume of the device, as well as the financial capabilities of the buyer. The market offers a wide selection of instrument models from both domestic and foreign manufacturers. However, it should be noted that if the purchase price for such devices as a closed-type expansion tank for heating is much lower than that of its main competitors, then it is better to refuse such a purchase.
Currently, the problem of buying an expansion tank for heating lies only in the correct selection of the type and volume of the device, as well as the financial capabilities of the buyer. The market offers a wide selection of instrument models from both domestic and foreign manufacturers. However, it should be noted that if the purchase price for such devices as a closed-type expansion tank for heating is much lower than that of its main competitors, then it is better to refuse such a purchase.
 The low cost indicates the unreliability of the manufacturer and the low quality of the materials used in its manufacture. Often these are products from China. As with all other goods, the price for a high-quality expansion tank for heating will not have a significant difference of about two to three times. Conscientious manufacturers use approximately the same materials, and the difference in price of models with similar parameters of about 10-15% is determined only by the location of production and the pricing policy of sellers.
The low cost indicates the unreliability of the manufacturer and the low quality of the materials used in its manufacture. Often these are products from China. As with all other goods, the price for a high-quality expansion tank for heating will not have a significant difference of about two to three times. Conscientious manufacturers use approximately the same materials, and the difference in price of models with similar parameters of about 10-15% is determined only by the location of production and the pricing policy of sellers.
 Domestic manufacturers have proven themselves well in this market segment. By installing modern technological lines in their production, they achieved the production of products whose parameters are not inferior to the best global brands at a lower cost.
Domestic manufacturers have proven themselves well in this market segment. By installing modern technological lines in their production, they achieved the production of products whose parameters are not inferior to the best global brands at a lower cost.
It should be borne in mind that it is important not only to buy an expansion tank for closed-type heating, but also to install it correctly.
 Having the necessary skills and following the instructions, you can install it yourself. If the technician still has any doubts about his knowledge, then it is best to turn to professionals to guarantee stable operation of the heating network and eliminate possible malfunctions.
Having the necessary skills and following the instructions, you can install it yourself. If the technician still has any doubts about his knowledge, then it is best to turn to professionals to guarantee stable operation of the heating network and eliminate possible malfunctions.
The lion's share of modern private houses and city apartments are equipped with a water heating system. In order for it to function stably without creating any problems, it is very important to competently approach its use and layout. We all know from school physics lessons that water tends to expand. To avoid unnecessary overload of the heating system, devices such as expansion tanks are used. Today we will take a closer look at them and find out how to install them correctly.

What it is?
Not every owner of a private house or apartment knows exactly what an expansion tank is. In this case, the name of this device speaks for itself - under conditions of a fixed mass of coolant in the heating circuit and pipeline, which are not elastic, with a change in the temperature of the coolant, the pressure level in the entire system will necessarily change. Here it is worth considering the fact that liquid expands when heated. The moment the force becomes stronger than the strength of the flow pipe/radiator, a serious accident will occur. Its main reason in this case will be the fact that water, when its volume changes under heating conditions, becomes almost incompressible. From this property comes the definition of water hammer.
The solution to such a serious problem is quite simple. It is necessary to place a special reservoir (expansion tank) in the heating system, equipped with a substance that can be easily compressed.
Under conditions of increasing water pressure and in the presence of the specified reservoir, the pressure will, of course, increase, but not very much.

Features and Specifications
As you can see, expansion tanks play one of the most important roles in the heating system. They extend its service life and avoid many serious problems.
Such items are used for the following purposes:
- play the role of a heating system, which operates using heat pumps and solar collectors;
- act as an autonomous heating system;
- are an independent system connected directly to the central heating, as well as a closed loop system.


Provided the temperature of the liquid in the heating system increases by only 15 degrees, due to expansion, the volume of the coolant becomes half a percent larger. The expansion tank is responsible for compensating for this expansion. An excess of coolant fluid penetrates into the tank itself. If the coolant cools down, the design of the tank squeezes out insufficient liquid back into the general system.
If there is a slight leak of liquid, so that the pressure in the system does not drop too much, the tank pushes away the coolant to compensate for the losses that have occurred.
In the case where the system is not equipped with an expansion tank, the expansion of the coolant provokes an increase in pressure. In addition, these processes certainly result in severe wear of the component elements of the entire system, and also lead to breakage and even rupture of pipes and taps.


The expansion tank has many positive characteristics that make it literally an indispensable element of a water heating system:
- thanks to this part there is no water pollution;
- most expansion tanks are inexpensive;
- ensure the reliability and safety of the entire system;
- allow you to avoid unnecessary heat losses;
- have the smallest amount of air in the system;
- in equipment responsible for heating, there can be any coolant - an expansion tank is allowed to be used in all cases;
- taps, pipes and radiators can last much longer if you use an expansion tank.



As for the direct volume of the expansion tank, it is worth considering that it directly depends on the specific type of coolant. We will look at how it can be calculated below.
Today in stores there are units whose size is:
- 5 liters;
- 10 l;
- 12 l;
- 19 l;


- 24 l;
- 35 l;
- 50 l;
- 80 l;
- 100 l.


Today there are several options for such devices. They are suitable for various heating systems and differ from each other in many respects.
Only their immediate purpose remains unchanged.


Design and principle of operation
Now we should consider in detail what elements the expansion tanks consist of and how they work. First, let's find out how such an element works.
Typically, the expansion tank structure as a whole is housed in a stamped steel housing. It has the shape of a cylinder. Cases in the form of peculiar “tablets” are slightly less common. Typically, high-quality metals coated with an anti-corrosion protective compound are used to produce these elements. The outer side of the tanks is covered with enamel.
For heating, expansion tanks with a red body are used. There are also blue versions, but this color is usually worn by water batteries, which are components of the water supply system.
They are not designed for high temperature parameters, and all their elements are subject to very high sanitary requirements.


On one side of the tank there is a threaded pipe. It is required to enable connection into the heating system. There are cases when the delivery also includes items such as fittings. They greatly simplify installation work.
On the other side, there is a special nipple valve. This element serves to generate the required level of pressure in the inside of the air chamber.
In the internal cavity, the expansion tank is divided into 2 separate parts by a membrane. Closer to the pipe there is a chamber intended for the coolant, and on the opposite side there is an air chamber. Typically, tank membranes are made of a very elastic material, which has minimal diffusion values.
This part is given a special shape, which is responsible for uniform deformation in the event of changes in pressure values in the chambers.

The principle of operation of the expansion tank in the heating system is very simple and understandable. Let's analyze it in detail.
- In the initial state, at the moment the tank is connected to the system and filled with coolant, a specific volume of water passes through the pipe into the water compartment. The pressure in both compartments gradually equalizes. Further, such a simple system becomes static.
- As the temperature value increases, there is a direct expansion of the coolant in volumes in the heating system. This process occurs accompanied by an increase in pressure indicators. Excess liquid is sent to the tank itself, and then pressure bends the membrane part. At this moment, the volume of the coolant chamber becomes larger, and the air compartment, on the contrary, decreases (at this moment the air pressure in it increases).
- When the temperature drops and the total volume of the coolant decreases, excess pressure in the chamber with air provokes a shift of the membrane back. At this time, the coolant returns back to the pipeline.


If the pressure parameters in the heating system reach critical levels, the valve should start, which belongs to the “safety group”. In such a situation, it will be responsible for releasing excess fluid. Certain models of expansion tanks have their own individual safety valve.
Of course, it is worth considering that the design of the tank mainly depends on the type of specific model purchased. For example, they can be non-separable or with the ability to replace the membrane element. Included with such products may be parts such as clamps for wall mounting or special stands - small legs with which it is easier to position the floor-standing unit on a flat plane.
Expansion tanks with a diaphragm membrane are usually non-separable. In many cases, they contain a balloon membrane part - it is made from pliable and elastic raw materials. At its core, this membrane is an ordinary water chamber. As pressure increases, it stretches and increases in volume. These types of tanks are usually complemented by a collapsible flange, which makes it possible to independently change the membrane if it breaks.
This fact does not affect the principle of operation in any way.


Kinds
Do not think that all expansion tanks have identical designs and performance characteristics. In fact, there are several varieties of such units. Each of them has certain distinctive features and structural features. Let's get to know them better.
Depending on the specific method of operation, tanks are divided into:
- open type heating tanks;
- closed expansion vessels.
Open options for expansion tanks are considered not the most popular. These units are installed in systems in which liquid circulation is not carried out in a forced mode (that is, without the use of a pump)
The open expansion tank has a lid that opens without any extra effort if you need to add water.


The main disadvantage of such a unit is that the coolant in it is associated with oxygen, and this provokes corrosion in the heating system. If there is not sufficient tightness in an open tank, then the water evaporates many times faster, so it has to be constantly topped up. According to experts, such a unit must be installed at the highest section of the heating system. It should be taken into account that carrying out such work is not always affordable.
A closed (or membrane) expander is fixed in a system where the movement of the coolant occurs forcibly - using a pump. A closed vessel is usually made in the form of a steel tank (it does not have a lid). It is equipped with a partition inside in the form of a rubber membrane. One half in such a model is needed to fill it with coolant, and the second is a place for air and nitrogen.
These containers are treated with paint in powder form in order to protect against damage to the walls of the housing under the influence of high temperatures.


On one side the tank itself is attached directly to the system using a fitting or flange. The opposite side is designed to pump air. The pressure indicator in a closed-type model makes it possible to automatically change the supply of coolant to the system and the tank itself.
Closed tanks are divided into:
- replaceable;
- non-replaceable.


Thus, replaceable tanks have a higher cost, but have significant advantages, which include:
- the ability to change the membrane if it is damaged or torn;
- the opportunity to save on pipes, since there is no need to install a closed tank at the top of the heating system;
- replaceable options are responsible for minimal heat losses;
- since the coolant does not “come into contact” with oxygen in any way, the pipes and the entire system as a whole are not subject to corrosion;
- the membrane can be positioned both vertically and horizontally;
- in this case there is no connection with the wall inside the metal tank;
- membranes can be replaced very easily and quickly (this is done through a flange).


Non-replaceable types of containers are cheaper, but the membrane cannot be changed in them if necessary. This element in the expander is installed as tightly as possible and is securely pressed against the inner walls of the tank. Damage or rupture of the membrane in this case can only occur if the system was started incorrectly (the pressure rises too quickly and is outside the normal range).
Depending on the type of membrane part, expansion tanks are divided into models with:
- balloon membrane;
- diaphragm membrane.
Thus, an expander with a balloon membrane is very durable and reliable. In addition, it has an impressive volume. In this case, the coolant does not come into any contact with the walls of the tank, so the appearance of rust on such products is excluded.
The flat heating expansion tank is equipped with a dividing partition made in the form of a diaphragm.

If it suddenly gets damaged, it will be possible to change it without much effort.
Materials
Various materials are used in the manufacture of expansion tanks, but the most common are models with a steel body.
Currently, many people, in an effort to save money, construct such units on their own. To do this, they often use sheet materials, which are subsequently assembled into a single structure by welding. You can also use the most unexpected items to make an expansion tank, for example, plastic barrels and canisters or old gas cylinders. The use of such materials significantly reduces the cost of creating an expansion tank. Despite such a large selection of suitable raw materials, experts still recommend turning to stainless steel if you plan to assemble the tank yourself.


As for the partition in such units, most manufacturers use high-quality rubber, synthetic rubber, natural butyl rubber or EPDM raw materials. Membrane elements for such units are made from various materials, which during use can easily withstand a wide range of temperatures.
If we consider specific cases, then:
- for tanks up to 2 thousand liters, membranes marked EPDM DIN 4807 are most often used;
- Tanks with a volume exceeding the above mark are equipped with BUTYL brand membrane elements.


How to choose?
The selection of an expansion tank must be approached very responsibly, since this product plays one of the most important roles in water heating systems.
Let us highlight a few simple tips that will allow the buyer to choose a suitable model of good quality.
- Experts recommend choosing membrane or closed containers. Despite the fact that these types of tanks are usually expensive, the heating system that contains them can last a very long time. This is explained by the fact that in this design the coolant and oxygen do not “meet” each other. But this is only advice - the choice, one way or another, remains with the owner of the home.
- Always pay special attention to the material from which the rubber partition is made in closed models.
Listed above are the raw materials that are usually used for their manufacture.


- If you are going to use the tank in conjunction with a central heating system, then the membrane rubber should have increased strength characteristics and resistance to high temperatures. This is because central heating in most cases does not involve significant pressure drops, but the temperature will still be quite high.
- A tank with a membrane characterized by increased elasticity can be safely purchased for a private heating system, since sudden pressure surges are common for this heating option.
- In order to use the expander not only in the heating system, but also in the system responsible for the water supply, the rubber from which the membrane is made must be food-grade. This is necessary so as not to detract from the positive qualities of the water.


- When choosing between non-replaceable and replaceable types of membranes, it is recommended to choose the former, since if a non-replaceable part is damaged, you will have to replace the entire unit instead of one element.
- Before purchasing an expansion tank, it is recommended that you carefully read its technical characteristics. Ask the seller for all necessary quality certificates. If the product does not have them or they do not want to present them to you, it is better to refuse the purchase.
- Don't forget to fill out the warranty card.
- Please note that one of the most important parameters that you should pay attention to when choosing a tank is its resistance to diffusion and temperature changes. In addition, all elements of the unit (from the housing to the membrane) must be made of high-quality materials.


Where to put it?
If there is forced circulation in the system, then the pressure at the connection site of the device will be equal to the static pressure at this point and at a given temperature condition (note that this rule only works if there is one membrane element). If we assume that it will change, then the result will be that in a closed system, a liquid that comes from incomprehensibly is formed, which is fundamentally wrong.
An open heating system is a container with a complex configuration that has special convection currents. Absolutely all components must guarantee the fastest possible rise of the hot coolant to the highest point. In addition, they must provide gravity drainage into the boiler involving radiators. Also, the design of such a system should not interfere with the passage of air bubbles to the top point.
Based on the above features, one conclusion should be drawn - the expansion tank must be fixed in the upper plane of the single-pipe system (usually on top of the accelerating manifold).


Calculation
To determine the volume of the expander, you can rely on several different methods. To do this, it is advised to contact specialists in special bureaus. As a rule, to carry out all the necessary calculations, they use special programs that allow them to take into account all the features and nuances that affect the operation of the heating system. However, it must be taken into account that the services of such specialists are in most cases expensive.
You can also calculate the volume of the tank yourself. To do this, use the generally accepted formula. In this case, you need to be as careful as possible, since even a small mistake can lead to incorrect values. When making calculations, it is important to take into account absolutely all the nuances: the volume of the heating system, the specific type of coolant, and even its physical properties.
In the given formula:
- C is the total volume of coolant in the system;
- Pa min – indicator of the initial absolute pressure in the tank;
- Pa max is the highest pressure parameter that can occur in the unit.



If you are afraid of making a mistake or you do not have time to carry out all the required calculations, then you should turn to the help of special online calculators. However, in this case, it is recommended to double-check the results obtained on several sites so as not to encounter incorrect operation of one or another portal.
Some people make it simpler - they estimate the necessary parameters by eye. In this case, the specific capacity of the heating system is equal to 15 l/kW. The result will be approximate values. But keep in mind that this method is only allowed during the feasibility study process.
Before purchasing a tank, of course, you only need accurate calculations.


DIY installation
Before proceeding with the installation of the expander, it is important to prepare:
- be sure to read the instructions before starting work;
- carry out all the necessary calculations of temperatures and pressure indicators (usually all this data is indicated in special reference books on standards for the use of units);
- prepare tools such as a wrench, a wrench for installing plastic pipes;
- if the tank has a large capacity, then you will also need to buy brackets - they will be useful for mounting.


When installing and connecting such units, you should rely on some recommendations from specialists:
- position the unit in such a way as to guarantee free access to it in the future;
- provide for the likely dismantling of pipes in the future;
- make sure that the diameter of the connecting pipe matches the connected water supply;
- correctly install the required temperature sensors;
- calculate the connection of shut-off valves.


Now you can proceed to the actual installation of the tank. It should be hung near the inlet of the flowing coolant in the direction of the heating unit.
Mark areas for fastening. Drill the required number of holes needed to secure the bracket. To do this, attach it to the wall and mark all areas of the connection. Having made all the necessary holes, you need to install anchor bolts in them, then hang the bracket and make sure that the fastening is secure. If everything is done efficiently, then you can install the tank itself, and then secure it with clamps.
Please note that such equipment cannot be installed in sub-zero temperatures. In addition, it is important to ensure that the air valve is in an accessible area after completion of installation work. This is necessary so that the owners have the opportunity to set the desired pressure level.
Absolutely all mechanisms that require adjustment must be in the public domain, and pipes must be located so that they do not create loads on the equipment.


As for such an element as a pressure reducer, it must be installed after connecting the measuring meter, so as not to encounter serious loads directed at the tank. This valve must be attached in front of the flow pipe.
After this, you need to configure the installed expansion tank. First you need to set the required pressure level. This must be done by pumping air. The pressure gauge will indicate when you need to stop. After this, water is pumped in using a pump, the pressure is equalized, and the membrane part is brought into a floating state. Then the tank can be considered ready for use. You may need to turn on the system and make sure it is working.
As you can see, the installation and connection diagram of the expansion tank is quite simple. Anyone can cope with such events.
The main thing is to rely on the instructions and be extremely careful at every stage.


Common problems
Expansion tanks, like any other heating units, are subject to a number of specific problems. Let's get to know them.
The most common breakdown of such units is the rupture of the membrane part. As a rule, this occurs due to too high pressure (above normal) or uneven loads. Please note that replaceable elements break much more often than compressed ones, since stronger materials are used for the latter, because they can be changed at any convenient time.
The problem of a damaged membrane can lead to many unpleasant consequences. For example, this often causes water to leak from the air valve.
If the membrane is not replaced in time, its rupture will lead to the fact that over time the tank will simply fail. This is due to the fact that liquid gets on the inner surface of the tank, after which it can become covered with rust and become unusable.


Please note that the old membrane should be replaced with the same part. It is advisable to contact a specialized service center for this.
Also, users quite often encounter damage to the tank body. If such a problem occurs with your equipment, it is better for you to seek help from a specialist. Do not attempt to repair damaged cabinet elements yourself, especially if you have never encountered such work before.
There are also cases when the expander boils. Most often, this problem occurs in homemade open-type structures. The main essence of this problem is the lack of circulation speed (or its complete absence).
Here are the main reasons for such breakdowns.
- Reduced wiring diameter. The main single-pipe heating circuit is usually installed with a pipe that is no less thin than DN 32.
- No slope. After the heating boiler, you need to make a so-called accelerating manifold. To do this, the pipe must be raised to the upper section of the circuit, where the expander is installed. The remaining part of the contour should be laid with a downward slope.


Many users are wondering how to fix such a serious problem without completely dismantling and reinstalling the heating system. The answer is simple - you need to install a circulation pump. This part works great in many systems (especially the open type). The pump must be placed on the return line directly in front of the boiler.
Another problem with expansion tanks is air blockage in the heating system circuit. To avoid colliding with it, you need to monitor the volume of water.
If you do not replenish it, the resulting evaporation will lead to the above problems.


How to replace?
From the above information we can conclude that the main problem with expansion tanks is a damaged membrane. Many users encounter this problem. Experts recommend replacing these elements in special service centers, but it is possible to carry out such work yourself.
This is done as follows.
- First you need to disconnect the tank from the heating system.
- Next, you need to reduce (reset) the pressure of the gas cavity using the nipple on top of the unit.
- Remove the diaphragm flange located next to the nozzle to connect the pipeline. By unscrewing the nut on top of the housing, you need to release the membrane part holder.
- Remove the membrane part from the cavity at the bottom of the housing.
- Next, you need to examine the surface of the interior of the hull structure. There should be no dirt or rust. If there are any, they must be removed and the surfaces washed with water. Then you need to dry the case.


- It is important to take into account the fact that the membrane is not resistant to oil. For this reason, products containing oil should not be used to ensure that the insides of the unit are protected from corrosion.
- Install the membrane element holder into the cavity located at the top of the membrane itself, if such fasteners must be present in the design of a particular device.
- Screw the bolt into the retaining element and place the membrane in the housing. The holder must be inserted into the cavity located at the bottom of the housing.
- The retaining part must be secured with a nut.
- Set the preliminary values for the air pressure in the expander. Check the structure for leaks, after which you need to connect the expander directly to the heating system.


Please note that if the safety valve operates with a high frequency, this may indicate that you have made a mistake with the selected volume. You may have made the necessary calculations incorrectly.
In order for the pipework to be installed according to all the rules, you need to pay close attention to the main components of the system: the area where the coolant enters directly into the container, as well as the place where it leaves.
To ensure that the water in the expansion tank never boils, choose loop pipes that have the correct diameter. In addition, it is important to take care of the slope of the contours.


Please note that if the vacuum expander will not function for a long time, then it must be kept only in a dry space, having drained the liquid from it in advance.
Check the unit at least once every six months for damage and defects. These include dents, rust or signs of leakage. If you suddenly discover such things, then you will need to eliminate the cause of their occurrence as soon as possible.
Remember that expansion tanks must be installed exclusively in accordance with the drawn up plan and diagram.
If you doubt your abilities, then it’s better not to take risks - turn to specialists.


In order to compensate for the 3% increase in coolant volume during heating to 70 degrees, an expansion tank is used for closed-type heating in the corresponding heating systems. You can visually distinguish the RB from the hydraulic accumulator (HA) of cold water supply systems by the red color of the body (HA tanks are blue).
Expansion tank for a closed heating system
In open (atmospheric) heating circuits, the expansion problem is solved in the following way:
- a container is mounted at the highest point of the circuit (usually an attic or attic);
- the excess volume of liquid flows under excess pressure into this container (tank);
- After cooling, the water flows back into the system under the influence of gravity + atmospheric pressure.
Open type expansion tank
The main disadvantage is the evaporation of water, the need for regular addition, and airing of the system. The sealed closed heating system is completely free of these disadvantages. To compensate for the expansion of the coolant, an expansion tank for heating of a closed type is used here; contact with the atmosphere is excluded.
Closed device in the system
The design and principle of operation of the tank
Membrane sealed tanks are much more convenient to use than open vessels. For cold water systems, the industry produces blue hydraulic accumulators (HA) that stabilize the pressure inside them. In heating circuits, a red expansion tank is used for heating of a closed type (RB), which eliminates “airing” of the circuit and is necessary to drain the water that has increased in volume during heating.
Design
Membrane tanks have a similar design, differing in details:
- HA - a rubber bulb is placed inside the hydraulic accumulator, repeating the contours of the internal chamber;
- RB - an expansion tank for closed-type heating is divided in half by a rubber partition (elastic material is usually rolled into a seam connection between the two halves of the body).
In 90% of cases, the RB has a cylindrical shape, however, there are modifications in the form of tablets for small volumes of coolant. When water is heated, the liquid expands and excess volume enters the tank.
The membrane material has a calculated elasticity; when the pressure decreases, it pushes the working fluid back into. Therefore, for tapping, it is enough to make a branch with a tee and mount it on the RB branch pipe.
Important! It is prohibited to install a red membrane tank immediately after the circulation pump.
Materials
HA uses food-grade rubber membranes, the shape of which completely eliminates contact of water with the walls of the metal casing. In RB the membrane is made of technical rubber, the inner surface of the tank is covered with anti-corrosion.
Thus, GA and RB are not interchangeable devices; they are intended for different operating conditions. If you install a blue tank in the heating circuit that is not designed for hot water, the service life of the system will be reduced. When installing a red tank in the cold water line, the water will no longer meet sanitary standards.
Tank parameters, calculation and selection criteria
The characteristics of the expansion tank for closed-type heating must meet the operational requirements. The easiest way to calculate the volume of RB is in the following way:
- fill the system with water;
- pour it into a calibrated container to calculate the volume of the coolant;
- multiply the resulting figure by a factor of 0.08.
Volume calculation
Thus, for a 100 liter heating circuit you will need a tank with a capacity of 8 liters. Another way to determine the volume of an expansion tank for closed-type heating is to calculate the heating power:
- to obtain 1 kW of thermal energy, about 15 liters of hot water are used in heating registers;
- knowing the thermal power required for the cottage, you can calculate the total volume of coolant;
- after which, calculate the volume of RB with the specified coefficient.
Helpful information! The proportions used are 17 l/kW, radiators 10.5 l/kW, convectors 7 l/kW.
In professional calculations, the formula is used:
V = (V s x K)/D , Where
D – equipment efficiency;
TO – expansion coefficient;
V s – volume of the system.
In turn, efficiency is calculated using the formula:
D = (P 1 – P 2)/(P 1 + 1) , Where
P2 – charging pressure;
P 1 – maximum pressure.
For a one-story building, the charging pressure corresponds to 0.25 bar (2.5 m high, respectively); for a two-story building it will be 0.5 bar. The maximum pressure is assumed to be equal to the characteristics of the safety valve (2.5 bar). Therefore, the value of D will be 0.64 or 0.57 for a one- and two-story house, respectively.
For example, for a system with a power of 22 kW (200 m2) 330 liters of coolant will be required, the volume of the RB tank will be 330 x 0.04/0.64 = 20.6 l.
Attention! The volume should only be rounded up, choosing the closest value in the manufacturer’s line.
Do-it-yourself tank installation, nuances
To eliminate water hammer inside the system, an expansion tank for closed-type home heating is installed, taking into account the requirements:
The best option is expansion tanks for closed-type heating on the return line in front of the boiler. There are stands for floor mounting and brackets for wall mounting:
- welded to the body;
- included in the kit; local assembly required.
To ensure the maintainability of the equipment, a ball valve is screwed onto the RB branch pipe, which allows you to remove the tank without disassembling the entire system (for example, to replace the membrane). Without taking into account the nuances of the boiler room layout, the general installation diagram looks like this:
- unpacking the expansion tank;
- installation of threaded fitting (“American”);
- installation of a ball valve;
- fastening the bracket with a band clamp (if the model does not have welded fasteners);
- wall or floor installation;
- releasing pressure from the system, draining the coolant;
- piping with a polymer (usually propylene), composite (metal-plastic) or steel pipe;
- pressure testing with working pressure;
- adjusting the pressure inside the air chamber (if necessary) using a car pump.
Helpful information! To seal threaded connections in pressure hot water and heating systems, Unipack linen winding is used. FUM tape is not intended for this.
There are brackets with safety groups that make it easier to install the radio in the correct position.
The air nipple is usually protected by a decorative cap with a threaded connection. Some modifications of the RB are equipped with a bleed valve, which allows you to relieve excess pressure into the sewer system.
The minimum coolant temperature is traditionally observed in the return line. After the water returns to the body inside the heating registers, it has almost room temperature in front of the boiler. If the RB is installed in this particular area, the effect of the aggressive environment on the anti-corrosion coating will be minimal, and the service life of the equipment will increase.
The pressure in the closed heating expansion tank is created after installation by a car pump. The main recommendations for this equipment are:
- upper coolant supply;
- installation at positive air temperatures;
- use of heat-resistant sealants.
Helpful information! In some boilers, the expansion tank of a closed-type heating system is built in by default. However, its volume may not be enough for specific operating conditions; calculation is still necessary.
Installing the RB in a hard-to-reach place will reduce the quality of equipment maintenance. The safety valve is not always included in the package, so you will have to purchase it separately. Corrosion on the outside of the housing is not a reason to replace equipment, but it is recommended to turn off the system, relieve pressure, and treat the defective areas with an anti-corrosion agent.
Replaceable membranes are controlled in accordance with the declared resource; the pressure inside the RB should be checked twice a year. The air chamber can be filled with inert gas, which will increase the performance of the tank.
Thus, you can calculate the volume of the expansion tank and install it inside a closed heating system on your own. It is enough to take into account the nuances given in this manual so as not to confuse the equipment with a hydraulic accumulator.
How to choose the right expansion tank (video)
You might also be interested in:
 Heating a private house without gas and electricity: a review of methods
Heating a private house without gas and electricity: a review of methods  How to choose a circulation pump for heating?
How to choose a circulation pump for heating?
The use of an expansion tank is necessary in every closed heating system, and even in some systems connected to central heating. The process of installing an expansion tank is quite complicated, but if you carefully study the instructions, doing it yourself, without involving specialists, is quite possible.
Operating principle of the expansion tank
The expansion tank is a metal tank that is connected to the heating system. The main function of this device is to eliminate the increase in pressure in the pipeline due to expansion of the coolant.

Expansion tanks come in two types: open and closed. The operating principle of each of these tanks differs from each other.
The open expansion tank has a metal lid that opens to add coolant to the system.
A closed expansion tank consists of a metal container that does not have any openings other than the connection to the system. The container is separated by an internal membrane made of rubber. When the pressure increases, the rubber bends and the coolant enters the tank; when the pressure decreases or the coolant leaks, the rubber presses on half of the tank in which the gas is located and the coolant enters the system. Thus, the expansion tank is a pressure regulator that prevents high voltage surges in the system. If you do not use an expansion tank, the heating system will not function properly, and taps, pipes and the boiler will quickly fail.
Expansion tanks are used in a private heating system, and in some cases also in a system connected to central heating.
Types of expansion tanks for heating
Expansion tanks are divided into:
- open,
- closed.

An open expansion tank has a number of disadvantages, so it is rarely used, mainly in cases where the system is not connected to a pump and water circulates freely.
Disadvantages of an open expansion tank:
- due to frequent opening of the lid, contact between components of the oxygen heating system occurs, which causes rust to form on the walls of pipes and radiators;
- when the water temperature rises, the liquid evaporates, so you should periodically add coolant to the system;
- an open expansion tank is installed at the highest point compared to the heating system, so installing such a device takes a lot of time.
The only advantage of an open expansion tank is its low cost compared to a closed one.
A closed expansion tank is called a membrane tank; depending on the type of membrane, there are:
- expansion tanks of replaceable type,
- non-replaceable expansion tanks.
Replaceable expansion tanks require replacing the membrane if damaged. To replace the membrane, simply unscrew the flange.
Non-replaceable expansion tanks mean replacing the entire tank if the membrane is damaged. Such tanks are more resistant to pressure changes, and the membrane fits perfectly and hermetically to the outer wall of the container.

Expansion tanks come in two forms:
- balloon,
- flat.
The balloon shape resembles a large container in which a membrane or lid is located, depending on the type of tank.
Flat expansion tanks have a flattened shape and a membrane in the form of a diaphragm. The advantage of flat expansion tanks is that they take up little space and are easy to install.
Calculation of expansion tank for heating
The size and volume of the expansion tank is affected by:
- system type;
- system capacity;
- maximum permissible pressure;
- installation location of the expansion tank.
The easiest way to determine the volume of the expansion tank is to find out the capacity of the heating system and divide this amount by 10%. For example, if the heating system contains 400 liters of coolant, then the volume of the expansion tank will be 40 liters if the coolant is water. If glycol fluid is used as a coolant, then another 50% must be added to this amount.

Please note that 3% of the coolant in the closed expansion tank goes to compensate for possible leaks. In any case, the volume of the tank obtained as a result of the calculation should be slightly increased.
To obtain an accurate calculation in large or complex heating systems, it is better to trust specialists or use an online calculator.
The correct design of the expansion tank is indicated by the failure of the safety valve.
Installation of an expansion tank for open heating
The open expansion tank is where water comes into contact with oxygen. An open container is used when water moves freely through the system without using a pump or when the system is connected to central heating.
Since air comes into contact with water, the entire heating system is designed at a slope so that excess oxygen is forced out of the radiators.
Expansion tank installation location: the highest point in relation to the heating system. The installation height of the expansion tank must exceed the installation height of the heating system.
Expansion tank installation diagram:

An additional expansion tank is installed if it is impossible to mount the heating system at an angle. The installation level of the main and additional expansion tanks must be the same.
The open expansion tank includes pipes:
- expansion,
- signal,
- circulation,
- overflow.
Using an expansion pipe, the tank is connected to the heating system.
In most cases, an open expansion tank is mounted near the boiler and connected to the water supply system using a signal pipe that monitors the coolant level.
The overflow pipe connects the tank to the sewer; when the tank overflows, the liquid is automatically drained into the sewer.
The circulation pipe ensures the supply of coolant if the expansion tank is located in an unheated room.

Installation of a closed expansion tank
Before studying the rules for installing a closed expansion tank, let’s consider the advantages of this device over an open expansion tank:
- minimal heat loss;
- do not need isolation;
- work at high pressure surges;
- installation anywhere, without reference to the highest point;
- closed type devices are more compact and easier to install;
- no rust formation on the internal walls of the heating system;
- ease of maintenance.
Tools for work:
- adjustable wrench;
- wrench for installing plastic pipes;
- step key.
The preparatory stage includes:
- disconnecting the boiler from electricity, gas or water supply;
- turning off the tap responsible for coolant circulation;
- draining the coolant from the heating section on which the expansion tank is installed.

Instructions for installing the expansion tank:
1. Install a shut-off and drain valve on the supply pipe to shut off and drain the water.
2. Connect the expansion tank to the system using screws or flanges. If the heating system pipes are polypropylene, you need to use a soldering apparatus, couplings, angles and fittings.
3. A fitting called “American” will help you easily remove the tank for replacement or repair in the future. Before installing the fitting onto the expansion tank, wrap linen tape around the threads and apply sealing paste.
4. When the water has been drained from the system, cut the pipe with special scissors and install a tee.
5. Install the safety valve and pressure gauge.
6. Before starting the system, clean the coarse filter.
7. Before connecting the expansion tank to the system, you need to create operating pressure. To do this, use a pump.
8. When the expansion tank is connected to the network, turn on all coolant supply taps and turn on the boiler.

1. Install the expansion tank so that the coolant flows from the top.
2. In the absence of data on the exact volume of the heating system, the capacity of the expansion tank is calculated based on the boiler power: 15 liters of liquid are calculated for 1 kW of power.
3. Before purchasing and installing an expansion tank, inspect the heating boiler. Many modern boilers have a hidden expansion tank, which is located in the middle of the boiler.
4. Do not install a closed expansion tank near the circulation pump, due to the occurrence of large pressure drops.
5. Installation of a vacuum expansion tank is carried out only at positive temperatures.
6. Installation of a closed type membrane expansion tank is carried out on the side of the cold water supply to the boiler.
7. As a sealant, use only those sealants that are resistant to high temperatures, otherwise leakage is inevitable.
8. When determining the location and installation of the expansion tank, you should think about the further approach or maintenance of the device. Do not install the expansion tank in hard-to-reach places.
9. When installing the expansion tank, follow safety rules and generally accepted instructions.
10. Be sure to read the manufacturer's instructions for installing the expansion tank.
11. Be sure to install a safety valve, which sometimes comes with the tank; if there is no valve, buy it separately.

Maintenance of the expansion tank for heating
1. Once every 6-7 months, the expansion tank should be inspected for mechanical damage or rust. If they are present, you need to fix the problem.
2. In closed expansion tanks, the pressure should be checked once every six months.
3. In devices with a replaceable membrane, the membrane must be periodically checked for integrity or damage.
4. If the expansion tank is not used for a long time, store the tank in a dry place, making sure to drain all water and dry the device.
6. It is best to use an inert gas such as nitrogen to fill the air chamber.
7. The correct operation of the expansion tank depends on the pressure and temperature of the heating system.

8. If the pressure drops sharply, there is a risk of damage to the membrane. To replace the membrane you need to perform a number of steps:
- disconnect the expansion tank from the system;
- relieve pressure in the tank using the valve located at the top of the tank;
- remove the flange located at the point where the tank is connected to the system;
- remove the membrane and drain excess water;
- insert the membrane and install the flange;
- attach the tank, having previously set the desired pressure.
Latest site materials
Well and well
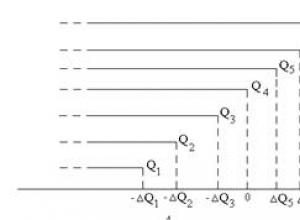
Scale of order of purpose for characteristics
Qualimetry is a field of science whose subject is quantitative methods for assessing product quality. The object of qualimetry is the quality of objects and phenomena of the real world, i.e. products, production processes, services and other activities of people,
Well and well

What does the name Yaroslav mean for a girl Yaroslav in Orthodoxy
The name refers to the ancient, even pre-Christian. The god of the harvest, Yarilo, was especially revered by the Slavs. This is how this name appeared, it consists of two words: “yar” - ardent, furious, strong and “slav” - glory. Literally, this is furious glory or bright glory.Old Slavonic names
cesspool

Chaos order gives birth to the game
Resistance to chaos is extremely common in our society, as in any society. People constantly resist chaos, investing a lot of emotions, thoughts and strength into it. It is a total and powerful tendency to fight uncertainty and
Faucets
How do our surroundings affect us?
We become like the people we interact with. Choose your environment - no matter how unique we are, it still affects us. Robert De Niro In his famous book Think and Grow Rich, Napoleon Hill writes about the power of repeating something.
Septic tank

Essay ideas and more
You are asking for an answer in the spirit of “no SMS and registration”. This doesn't happen. I have not seen a single book or series of books that would cover physics from scratch to postgrad level. Basically, any topic has its own good canonical textbook. If this is physics
